As we edge closer to 2025, inflation is shaping up to be one of the most critical forces affecting economies worldwide. Whether you're a savvy investor, a small business owner, or just someone trying to make ends meet, understanding inflation is more important than ever. Inflation in 2025 won't just tweak the numbers on your bank statement—it could change the way we all live, work, and plan for the future. This article is here to break it all down for you, offering insights into what's causing inflation, how it affects our lives, and what we can do about it.
Inflation is one of those topics that tends to get complicated fast. But let's face it: it's something we all need to wrap our heads around. Historically, inflation has acted like a seesaw—it can keep things balanced when managed well, but when it gets out of control, it can wreak havoc. As we approach 2025, experts are warning that inflation could become a dominant player in shaping economic policies around the world. This article aims to give you a clear, no-nonsense overview of inflation trends, so you can navigate the challenges ahead and even spot some opportunities along the way.
By the time you finish reading this, you'll have a better grasp of how inflation impacts global markets, consumer behavior, and investment strategies. If you're looking to protect your hard-earned money or explore new ways to grow it, this guide is your ticket to understanding the economic landscape of 2025. So, buckle up and let's dive in.
Read also:Why The Chicago Bears Are Eyeing A Top Lineman A Gamechanging Move
Table of Contents
- What is Inflation?
- Causes of Inflation
- Effects of Inflation on the Economy
- Global Inflation Trends
- Inflation Forecast for 2025
- Impact of Inflation on Consumers
- Investment Strategies Amid Rising Inflation
- Government Policies to Combat Inflation
- Historical Perspective on Inflation
- Conclusion
What is Inflation, Anyway?
Let's start with the basics. Inflation is what happens when the prices of the things we buy—groceries, gas, rent, you name it—go up over time. When inflation kicks in, your money doesn't stretch as far as it used to. For example, if a gallon of milk cost $3 last year and now costs $3.50, that's inflation at work. Economists measure inflation using tools like the Consumer Price Index (CPI) or the Producer Price Index (PPI), which track how prices change for different goods and services.
Now, here's the kicker: a little bit of inflation isn't necessarily a bad thing. In fact, moderate inflation is often seen as a sign of a healthy, growing economy. It means businesses are thriving, people are spending, and the economy is moving forward. But when inflation gets out of control, it can cause all sorts of problems. Savings lose value, people start cutting back on spending, and the whole system can start to unravel.
Types of Inflation
- Creeping Inflation: This is the slow and steady kind of inflation, usually under 3% per year. Think of it as the tortoise in the race—slow but steady.
- Walking Inflation: When inflation starts picking up the pace, usually between 3% and 10%, it's called walking inflation. It's like the economy is jogging instead of walking, and things can start to get a little tricky.
- Galloping Inflation: Once inflation hits double digits—say, over 10%—it's time to worry. Galloping inflation can throw economies into chaos, making it hard for people to plan for the future.
- Hyperinflation: This is the worst-case scenario, where prices skyrocket out of control, sometimes doubling in just a matter of weeks or even days. Think of it as a runaway train that can completely collapse an economy.
What Causes Inflation?
Inflation doesn't just happen overnight—it's usually the result of a mix of factors. There are three main types of inflation, each with its own set of causes: demand-pull, cost-push, and built-in inflation. Let's break them down:
Demand-Pull Inflation
Demand-pull inflation happens when there's more demand for goods and services than there is supply. Imagine this: everyone suddenly wants to buy the latest smartphone, but the factories can't make enough to keep up. As a result, the price of that phone goes up. This type of inflation often occurs during times of strong economic growth, when people have more money to spend and businesses struggle to meet the rising demand.
Cost-Push Inflation
Cost-push inflation happens when the costs of producing goods and services go up, forcing companies to charge more. Think about it this way: if the price of oil goes up, it costs more to transport goods, and those extra costs get passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices. Other factors, like rising wages or supply chain disruptions, can also contribute to cost-push inflation.
Built-In Inflation
Built-in inflation, also known as the wage-price spiral, is a bit more complicated. It happens when workers demand higher wages to keep up with rising living costs. Employers then pass those higher wages on to consumers in the form of higher prices, which in turn leads to even higher wages—and the cycle continues. It's like a never-ending game of tag, where prices and wages keep chasing each other.
Read also:Milano Cortina Elevating Your Home With Italian Elegance
How Does Inflation Affect the Economy?
Inflation has a ripple effect that touches just about every part of the economy. Depending on how high inflation gets, it can either help or hurt. Let's take a look at both sides of the coin:
Positive Effects
- Encourages Spending: When people think prices are going to keep going up, they're more likely to spend now instead of later. This can give the economy a boost, as businesses see more sales and hire more workers.
- Reduces Debt Burden: Inflation can actually be a good thing for people who owe money, like homeowners with mortgages. Over time, inflation erodes the real value of debt, making it easier to pay off.
Negative Effects
- Reduces Purchasing Power: This is probably the biggest downside of inflation. As prices rise, your money doesn't go as far as it used to. That means you might have to cut back on things you enjoy, like eating out or taking vacations.
- Uncertainty and Instability: High inflation can create a lot of uncertainty, making it harder for businesses to plan and invest. It can also lead to social unrest if people feel like they're losing ground financially.
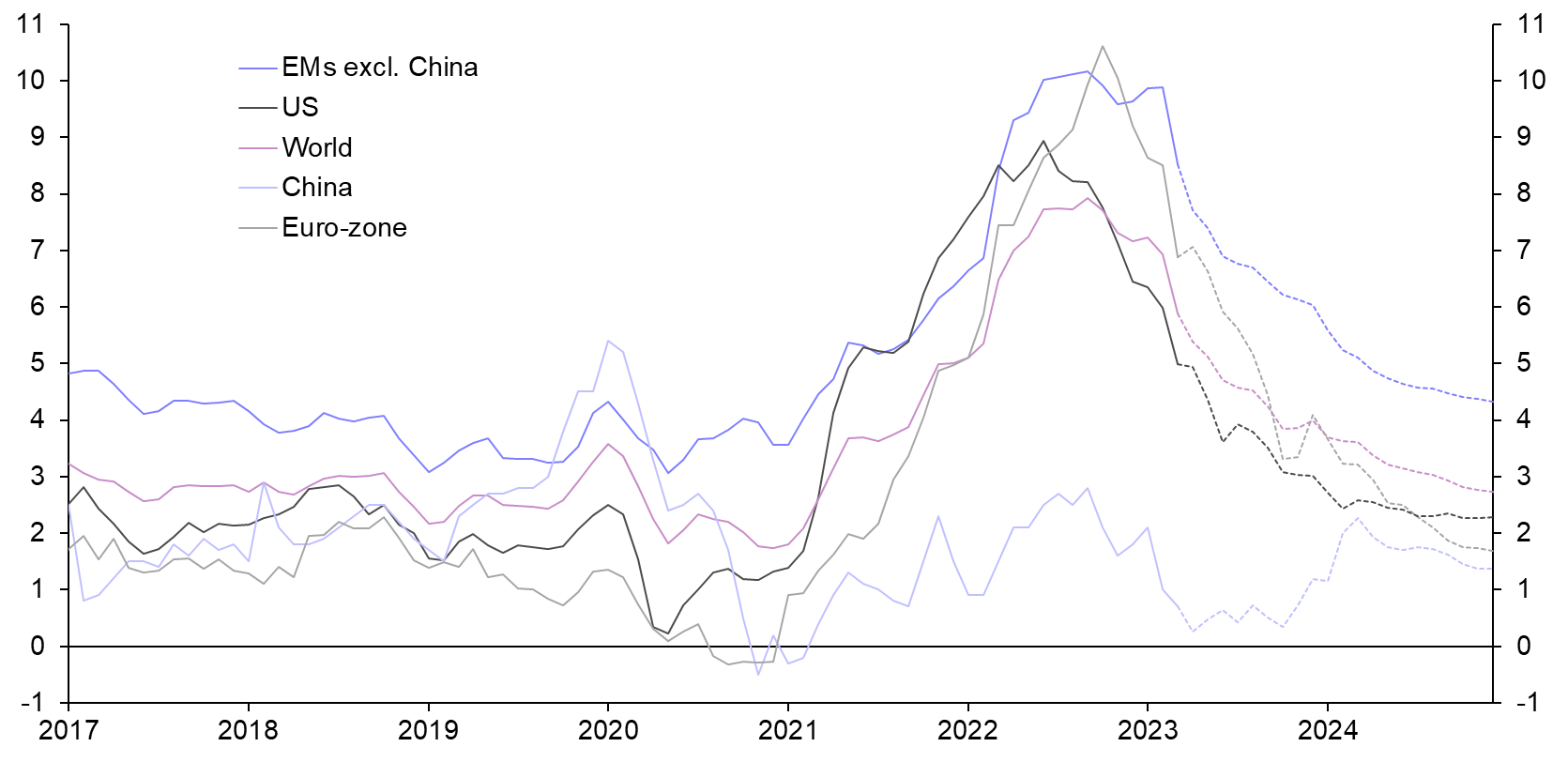
Global Inflation Trends
Inflation isn't just a local issue—it's a global one. Different parts of the world are experiencing inflation in different ways, depending on things like monetary policies, geopolitical events, and technological changes. In recent years, we've seen inflation rising in many places, partly because of disruptions in global supply chains and rising energy costs.
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is predicting that global inflation will stay high through 2025, with developing countries feeling the brunt of it more than advanced economies. This is a big deal, because it means countries need to be proactive in managing inflation to avoid long-term damage to their economies.
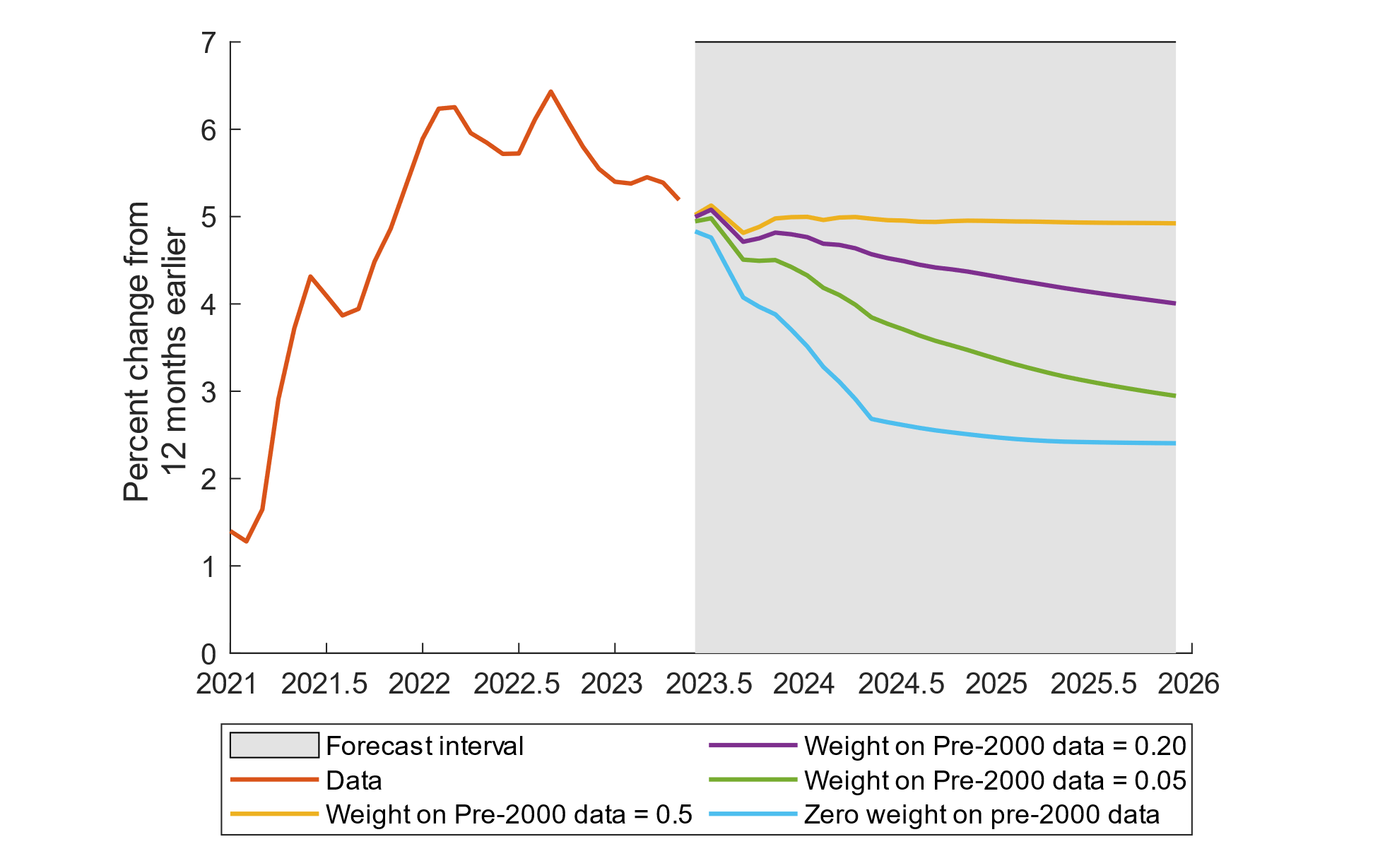
What's the Forecast for Inflation in 2025?
Looking ahead to 2025, most economists agree that inflation is going to be a major issue. There are a few key factors driving this forecast:
- Central Bank Policies: Many central banks are likely to keep their monetary policies loose to help economies recover from the pandemic. While this can be good for growth, it can also fuel inflation.
- Supply Chain Challenges: Supply chains are still recovering from the pandemic, and any new disruptions could lead to higher production costs, which would drive prices up even further.
- Energy Prices: The global energy market is unpredictable, and big swings in oil and gas prices could have a major impact on inflation, especially in countries that rely heavily on imported energy.
While forecasts vary, one thing is clear: we need to take steps now to manage inflation and minimize its impact on our lives.
How Does Inflation Affect You?
Inflation hits consumers right where it hurts—right in the wallet. As prices go up, you might find yourself spending more on essentials like food, housing, and healthcare, leaving less room for the things you enjoy. To cope with inflation, you can take steps like creating a budget, building up your savings, and investing in assets that can protect you from rising prices.
But staying informed is just as important. Keeping an eye on economic trends and understanding government policies can help you make smarter financial decisions. Knowledge is power, after all.
Investing in a World of Rising Inflation
If you're an investor, inflation can be both a challenge and an opportunity. The key is to diversify your portfolio and focus on investments that tend to do well during inflationary periods. Here are a few strategies to consider:
- Real Assets: Things like real estate, commodities, and precious metals can act as a hedge against inflation. When prices go up, these assets often increase in value.
- Stocks: Companies with strong pricing power and solid business models tend to perform better during inflationary times. Look for businesses that can pass on higher costs to their customers without losing sales.
- Inflation-Linked Bonds: These bonds adjust their value based on inflation, offering protection against rising prices. They're a great way to safeguard your portfolio against the effects of inflation.
Of course, everyone's financial situation is different, so it's always a good idea to consult with a financial advisor to tailor your strategy to your goals and risk tolerance.
How Governments Tackle Inflation
Governments and central banks have a variety of tools at their disposal to manage inflation. Here are some of the most common approaches:
- Interest Rate Adjustments: Central banks can raise interest rates to make borrowing more expensive, which slows down spending and helps bring inflation under control.
- Fiscal Policies: Governments can use tax reforms and spending cuts to reduce inflationary pressures. For example, they might cut taxes to give people more disposable income or reduce spending on certain programs to rein in government deficits.
- Monetary Policies: Central banks can also adjust the money supply through measures like quantitative tightening, which reduces the amount of money in circulation and helps stabilize inflation.
Of course, implementing these policies effectively requires careful monitoring of economic indicators and close collaboration between governments and central banks. It's a delicate balancing act, but when done right, it can make a big difference.
Learning from the Past
Inflation has been around for a long time, and history has plenty of lessons to teach us. From the hyperinflation of the Weimar Republic in the early 20th century to the stagflation of the 1970s, we've seen how inflation can shape economies in profound ways. By studying these historical trends, policymakers and economists can better anticipate challenges and develop strategies to mitigate inflation's impact.
Understanding the historical context of inflation is crucial for anyone trying to make sense of the current economic landscape. It helps us see the bigger picture and appreciate the complexities of managing inflation in today's interconnected world.
Wrapping It Up
Inflation in 2025 is going to present both challenges and opportunities for economies and individuals around the globe. By understanding its causes, effects, and potential solutions, you can better navigate the changing economic landscape. Whether through careful financial planning, smart investments, or informed policy decisions, managing inflation is key to long-term success.
We'd love to hear your thoughts and insights in the comments below. And if